Floor Slabs AS 3600 attempts to limit the magnitude of longterm deflection to ensure that floors remain serviceable during the life of any building Code requirements over the past 40 years have become increasingly more stringent, and longterm deflection design is the governing performance criterion for office and similarly loaded floor slabs Good practice for ground floors Ensure all thermal and cold bridging is eliminated around the external perimeter of the floor Ground bearing slabs must have a suitable damp proof membrane which can be placed above or below the insulation Suspended floors should incorporate a ventilated void below the floor with a minimum height of 150 mm Click to see full answer Also to know is, what is a suspended ground floor?

Method Statement For Construction Method Statement Non Suspended Slab
Non suspended floor slab
Non suspended floor slab- A suspended floor is a ground floor with a void underneath the structure The floor can be formed in various ways, using timber joists, precast concrete panels, block and beam system or cast insitu with reinforced concrete However, the floorCauses of foundation or floor slab settlement Broken sewer line, water line, or floor drain under the floor slab Failure to compact the soils properly during construction Trees sapping the ground water under the foundation A plumbing pipe beneath the floor slab of this residence broke Water from the damaged pipe washed away a proportion of




2 2 Structural Element Reinforced Concrete Slabs Ppt Video Online Download
Firstfloor slab thickness The normal thickness used for reinforced concrete slabs in South Africa is 170 mm for small slabs, 255 mm for slabs larger than 5m x 5m and 340 mm thick for longspan slabs forming part of a beam and carrying heavier loads The thickness of a slab will depend on the use and span of the slabA concrete slab is a common structural element of modern buildings, consisting of a flat, horizontal surface made of cast concrete Steelreinforced slabs, typically between 100 and 500 mm thick, are most often used to construct floors and ceilings, while thinner mud slabs may be used for exterior paving In many domestic and industrial buildings, a thick concrete slab supported on foundations or directly on the subsoil, is used to construct the ground floor These slabs Suspended Slab Formwork what is it and applications Suspended slab formwork is formed and cast onsite, and this is done with removable or nonloadable formwork s or permanent formwork s that form part of the reinforcement Therefore, to produce a suspended slab formwork, we need precise formwork, which can be selected from two different types
3 Pour, Compact and Finishing Concrete Floor Slab; Traditional ground floors have consisted of little more than a few flagstones or bricks placed directly over the soil The Victorian era saw the widespread introduction in mass housing with suspended timber floors, alongside rudimentary solid floors in hardwearing areas such as kitchens and hallways This combination persisted well into the 1930s, with solid concreteSuspended floors are normally made up of 2 materials, either timber joists or a concrete beam system There are quite a lot of variations on these types of floor, mainly depending on what use you intend for that floor area and the floor finish In recent years the use of suspended concrete floors has become common
2 V10 • Composite and NonComposite Design Guide wwwascsdcom 11 Panel Features and Benefits Composite deck 3 inch deep, 36 inch coverage, 10 foot to 14 foot Optimal Span Range No Acustadek® Options Proven for 10 to 14 foot span conditionsA floor that is made of timber or other material is not referred to as a floor slab Concrete slabs that form the ground floor of a building may be either supported on beams (called a suspended slab) or supported directly on the subsoil, (via hardcore, for example) called a Suspended Slabs are typically buildup in two ways 1 Precast concrete Unlike onsite concrete pouring, a leading manufacturing approach is used to produce highquality precast concrete in a restrained factory environment The reinforcement is placed in reusable and adjustable molds, and the concrete is poured, vibrated and cured



Non Suspended Slab Is A Slab That Cast On The Ground The Method To Design This Slab Is Different Than Suspended Slab How To Design A Non Suspended Slab Quora




Suspended Floors All You Need To Know Thermohouse
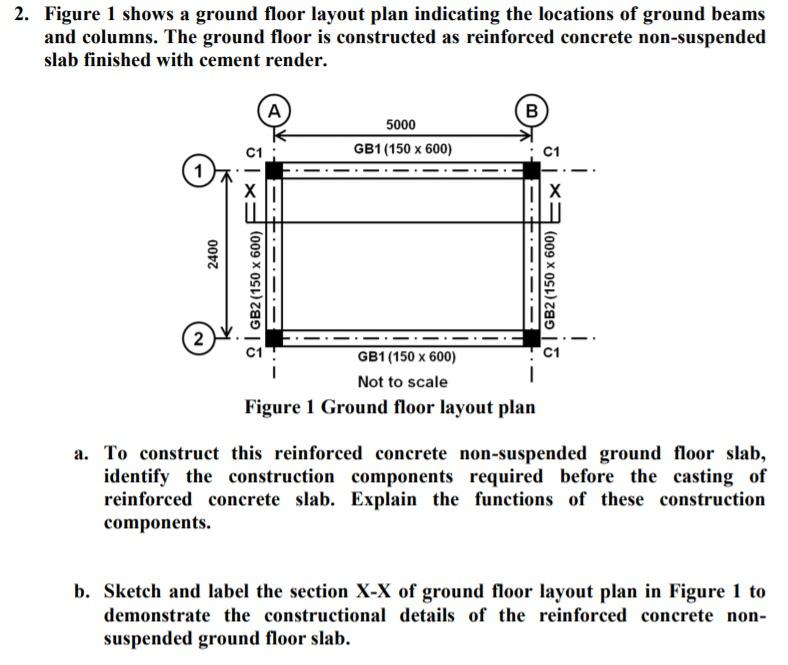
Construction sequence Questions send it to megadethigorot@gmailcom (No need to subscribe or comment if you don't want to ask in public just send a messagFigure 1 shows a ground floor layout plan indicating the locations of ground beams and columns The ground floor is constructed as reinforced concrete nonsuspended slab finished with cement render A B 5000 GB1 (150 x 600) C1 х Х 2400 2 GB2 (150 x 600) 2 GB2 (150 x 600) GB1 (150 x 600) Not to scale Figure 1 Ground floor layout plan a For a 5" thick slab a 6x6W55xW55 mesh will serve For 3 1/2" slab a 6x6W40xW40 will do Anything less is a very bad idea I never spec slabs less than 5" on my projects If the slab is also the finish floor the minimum crack control numbers above are NOT sufficient for a satisfying visual end result



Suspended Slab And Beam Youtube
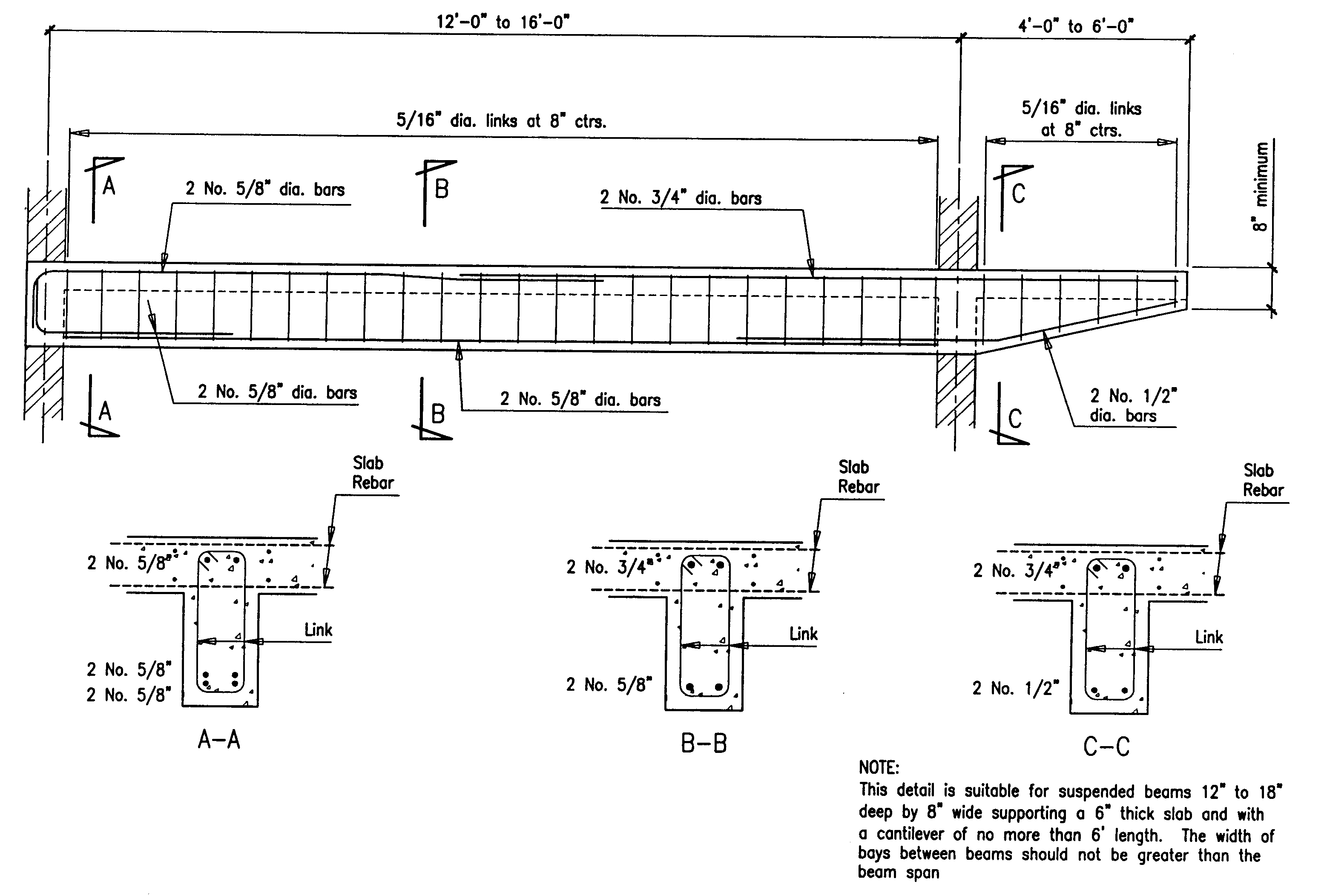



Building Guidelines Drawings Section B Concrete Construction
The foundation perimeter vertically extends approximately 1/2″1″ above the slab While the perimeter is level, the concrete slab is uneven, hence the 1/2″1″ inch variance The plan is to hang 2×10 joists (using ledger board and joist hangers) 15″ above the foundation perimeter so that the floor will be at the same level as theSlab foundation repair using slab jacking or foam jacking typically costs less than a third the cost of replacement Foam jacking minimizes the cost of flooring repairs because the injection holes are small (dimesize) and relatively infrequent For example, for tiled floors, we can drill holes at the fourway intersections of tiles in the Selection of floor system Actual floor systems in buildings come in all sizes, shapes, and forms There are so many variables to any floor system such as different spans, offset spans, cantilevers, and the extent of continuity, the effects of beams, columns and walls on the slab system, etc that it is difficult to cover all situations in a limited series of charts




2 2 Structural Element Reinforced Concrete Slabs Ppt Video Online Download
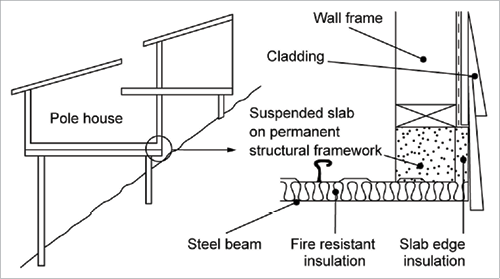



Concrete Slab Floors Yourhome
Nonsuspended slabs sit directly on the ground A concrete slab is a common structural element of modern buildings, consisting of a flat, horizontal surface made of cast concrete E2/AS1 gives minimum heights of finished floor levels above ground for concrete slab floors and suspended timber floors, the measurements depending on whetherOnce completed and cured it is put in place by cranes or jacks, then suspension components are attached This includes liftslabSimply, a floor slab functions to distribute without deformation or cracking, the loads applied to it to the weaker subgrade below, in the case of a ground bearing slab, or to the piles supporting it if designed as a suspended ground slab, and to provide a suitable wearing surface upon which the operations in the facility may be carried out efficiently and safely




Building Construction Ii Ecm 3154 Week 1 Floor




Jobsite Conditions John Cox Lumber Co Blog
Suspended concrete slabs are generally constructed in two ways * Precast The slab is constructed in forms elsewhere; Suspended vs Non Suspended TT on Concrete Floor Am considering purchasing a Clearaudio Reference or Master Reference table that would sit on a large Polycrystal amp stand The stand will sit directly on a carpeted concrete slab basement floor The speakers, which are about even w/ the turntable are about 9ft apart (45 from the table)Figure 2 Suspended timber floor with floorboards removed For most heritage properties, the most effective and appropriate way to insulate a suspended floor and improve its airtightness is to retrofit insulation beneath the floorboards, between the supporting joists (figure 2) See our detailed installation guide for more details




How Are Suspended Slabs Built Build




How Are Suspended Slabs Built Quora
For design of slabsonground, with the exception of highway and airport pavements, parking lots, and mat foundations 122 ACI Committee 302develops recommendations for construction of slabonground and suspendedslab floors for industrial, commercial, and institutional buildings ACI 3021R provides guidelines and recommendations onThe Speedfloor suspended concrete floor system uses a cold formed steel joist as an integral part of a Speedfloor combines a concrete slab with a rollformed galvanised steel joist for permanent structural It is the compression element of the noncomposite joist during constructionComposite floor systems In the final state the ribs in the decking serve as void formers in the slab, thereby reducing the weight of floor construction with the knockon benefits this can have It is also possible to suspend services from the soffit of a composite slab, using anchors that are designed to slot into the decking profile



1




Assignment 2 Edited
Tolerances for Suspended Concrete Slabs ASCC Position Statement #24 Concrete floors are often placed on a suspended structural system consisting of a metal deck supported by openweb steel joists, steel beams, or precast concrete members Tolerances for the floors placed on these suspended systems are often misunderstood ACIA wet floor may cause accidental slips, trips, and falls and can be very dangerous for forklift and other machinery as they may be unable to brake or stop when needed Most often, the cause of a damp concrete floor can be explained as Sweating Slab Syndrome Most times Sweating Slab Syndrome is accompanied by concrete efflorescence4 Curing Concrete and Remove Formwork




Types Of Slab Youtube




Method Statement For Construction Method Statement Non Suspended Slab
Nonsuspended slab is a slab that cast on the ground The method to design this slab is different than suspended slab How to design a nonsuspended slab? Some suspended slabs are solid, while some have hollow sections to reduce weight and allow the running of services through the slab A thinner but still nonwood alternative is fibrecement sheeting This is similar to cement sheeting used for wall cladding, but is thicker and stronger and can be used as a loadbearing floor directly OneSlab R‐Value Table Insulation and Fenestration Requirements by Component E ClimateZone Slab R‐valued 4 10, 2 ft 5 10,2 ft 6 10,4 ft 9 d R‐5 shall be added for heated slabs Heated slab slab‐on‐grade construction in which the heating elements are in contact with, or placed within or under the slab




Insulation Retrofit For An Existing Concrete Slab And 2x4 Walls Greenbuildingadvisor



Farm Structures Ch5 Elements Of Construction Floors Roofs
Some contractors find that embedding the ma f CONCRETE FLOOR AND SLAB CONSTRUCTION 3021R39 terials and restraightening can be accomplished in one step 871 Bonded monolithic twocourse floors—For these using a modified highway straightedge floors, the topping course is placed before the base course 9 When slabs on ground are polished, nonuniform exposure of aggregate is a result of high spots cause by slab curling Deflection of many suspended slabs exceeds the upward movement at curled slabs Suspended slabs differ from nonsuspended slabs because they are suspended above the ground via beams Nonsuspended slabs sit directly on the ground




Figure B 10 Figure B 10 Alternative Floor Slab Detail The Suspended Reinforced Concrete Garage Workshop Plans Concrete Structural Drawing



1
Suspended slabs have movement joints, referred to by most as expansion joints, but their purpose is mostly for contraction In order to accomodate the different volume changes between a long structural wall and a continuous floor slab, we detailed a slip joint at the ledge and cased the first 6" of reinforcement in pipe insulation to allow2 Prepare and Place Reinforcement for Slab;This chapter gives guidance on meeting the Technical Requirements for suspended ground floors including those constructed from insitu concrete precast concrete timber joists 521 Compliance 522 Provision of information 523 Contaminants




Concrete Slab Wikipedia
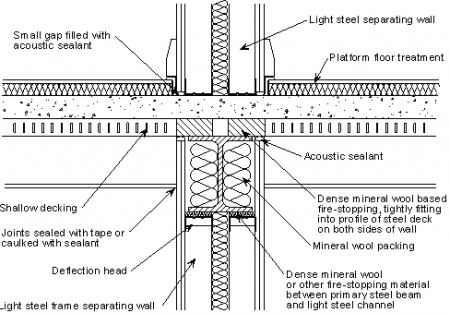



Floor Systems Steelconstruction Info
Suspended slabs are made of concrete and steel mesh, the same as a ground slab They are normally prefabricated offsite, and transported by truck Some slabs have hollow channels running through them these 'hollow core slabs' are used to help reduce weight, and also to allow cabling and piping to be run through the slabA suspended floor is a ground floor with a void underneath the structure The floor can be formed in various ways, using timber joists, precast concrete panels, block and beam system or cast insitu with reinforced concrete However, the floor structure is supported by external and internal walls RE Suspended Slab Cracking ataman (Structural) (OP) 4 Hi, There is negative reinforcement over the walls and beams The slab is predominantly supported on r/c walls so it is a slab on stiff supports The beam spans are not large, probably 10 feet max The cracks do go over the beams, walls etc




Ground Level Concrete Slab Subfloor Build




Radiant Floor Heating Tubing Installation Methods Radiantec
Concrete Floor Slab Construction Process 1 Assemble and Erect Formwork for Slab;CONCRETE FLOOR AND SLAB CONSTRUCTION 3021R3 The design of slabsonground should conform to the recommendations of ACI 360R Refer to ACI 223 for procedures for the design and construction of shrinkagecompensating concrete slabsonground The design of suspended floors should conform to requirements of ACI 318 and ACI 4211RThe Suspended Slab With Sleepers Method two involves laying down sleepers in order to raise the floor and create a channel for the radiant tubing Sleepers can take many forms depending upon which size of radiant tubing is used If headroom is critical, then ½" PEX tubing on 8″ centers is commonly used with sleepers made from 4″ wide
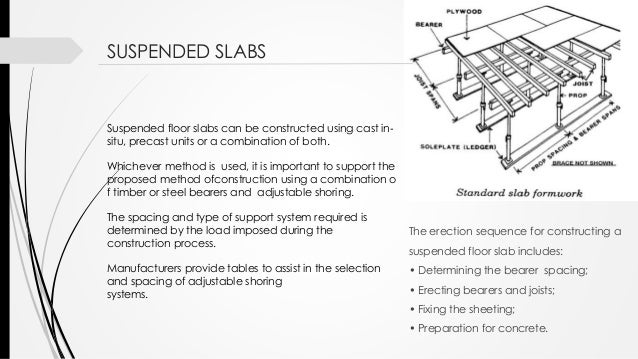



Formwork Construction In Structures




Concrete Slab Abis
To form this type of slab requires temporary beams, columns, and plywood as floor supports for the concrete The forming is very similar to that of framing floor of a house except concrete is a lot heavier than normal residential live load and dead load
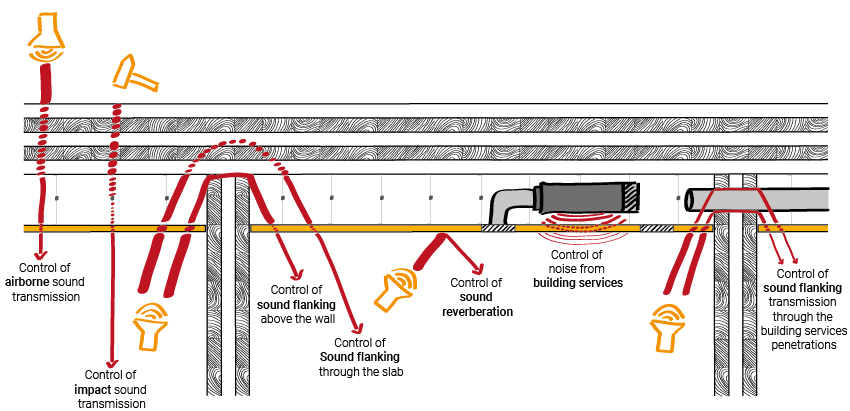



The Acoustic Design Implications Of Exposing Clt Floor Slabs Atelier Crescendo Acoustic Consultancy



Suspended Slab Subfloor Build




Concrete Slab Types Construction Cost And Applications The Constructor
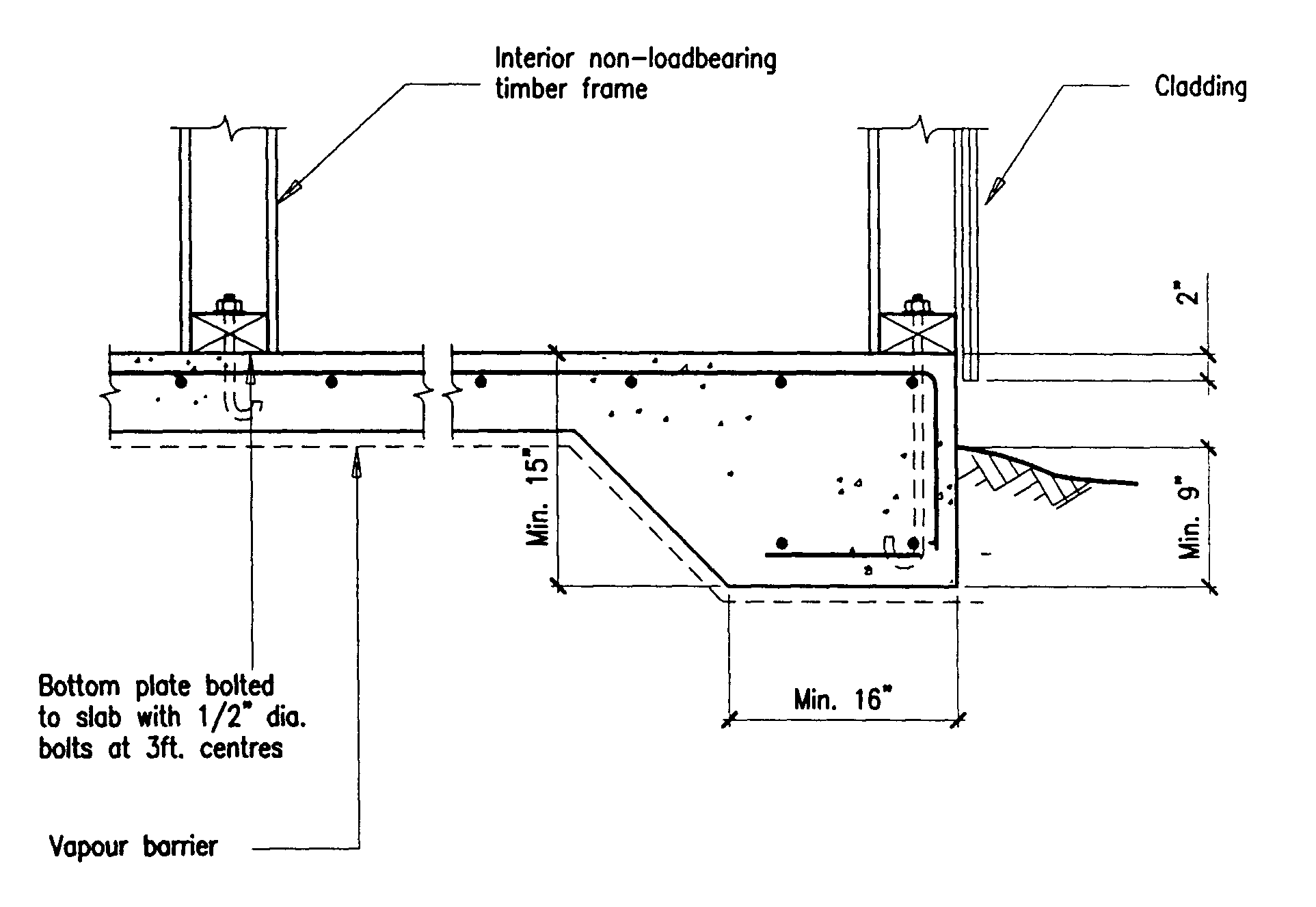



Building Guidelines Drawings Section B Concrete Construction




6 Ground Floors Construction Studies



2 Figure 1 Shows A Ground Floor Layout Plan Chegg Com




Method Statement For Construction Method Statement Non Suspended Slab



Suspended Slab For Housing On Expansive Clay Download Scientific Diagram




Monolithic Definition Monolithic Footing Monolithic Slab Foundation Advantages Disadvantages Of Monolithic Slab Foundation Monolithic Slab




Non Suspended Slab Non Suspended Slab الهندسة والمعلومات Facebook




Response Of Building Systems With Suspended Floor Slabs Under Dynamic Excitations Sciencedirect




Concrete Slab Wikipedia




Concrete Floor Slab Construction Process The Constructor




Response Of Building Systems With Suspended Floor Slabs Under Dynamic Excitations Sciencedirect



Concrete Slab Floors Yourhome



How To Design One Way Slab As Per Aci 318 19 Example Included The Constructor




Ground Slabs Introduction



Concrete Slab Floors Yourhome




Method Statement For Construction Method Statement Non Suspended Slab




Concrete Slab Wikipedia




6 Ground Floors Construction Studies




Method Statement For Construction Method Statement Non Suspended Slab




Floor Slab An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Suspended Slabs




Floating Floors Vs Non Floating Floors What Gives




Kumpulan Rahman Brothers Progress Report 5




Floating Slab Vs Monolithic Slab What Is Monolithic Slab What Is Floating Slab




Method Statement For Construction Method Statement Non Suspended Slab




Response Of Building Systems With Suspended Floor Slabs Under Dynamic Excitations Sciencedirect




Ground Bearing Floor Slab 650x368 Png Download Pngkit




Non Suspended Slab Non Suspended Slab الهندسة والمعلومات Facebook



Why Polishing Suspended Concrete Slabs Is More Likely To Disappoint Customers For Construction Pros




Pdf Fill Compaction And Its Consequences Of Non Compliance Semantic Scholar




Concrete Slab Floors Yourhome



Farm Structures Ch5 Elements Of Construction Floors Roofs




Why Polishing Suspended Concrete Slabs Is More Likely To Disappoint Customers For Construction Pros
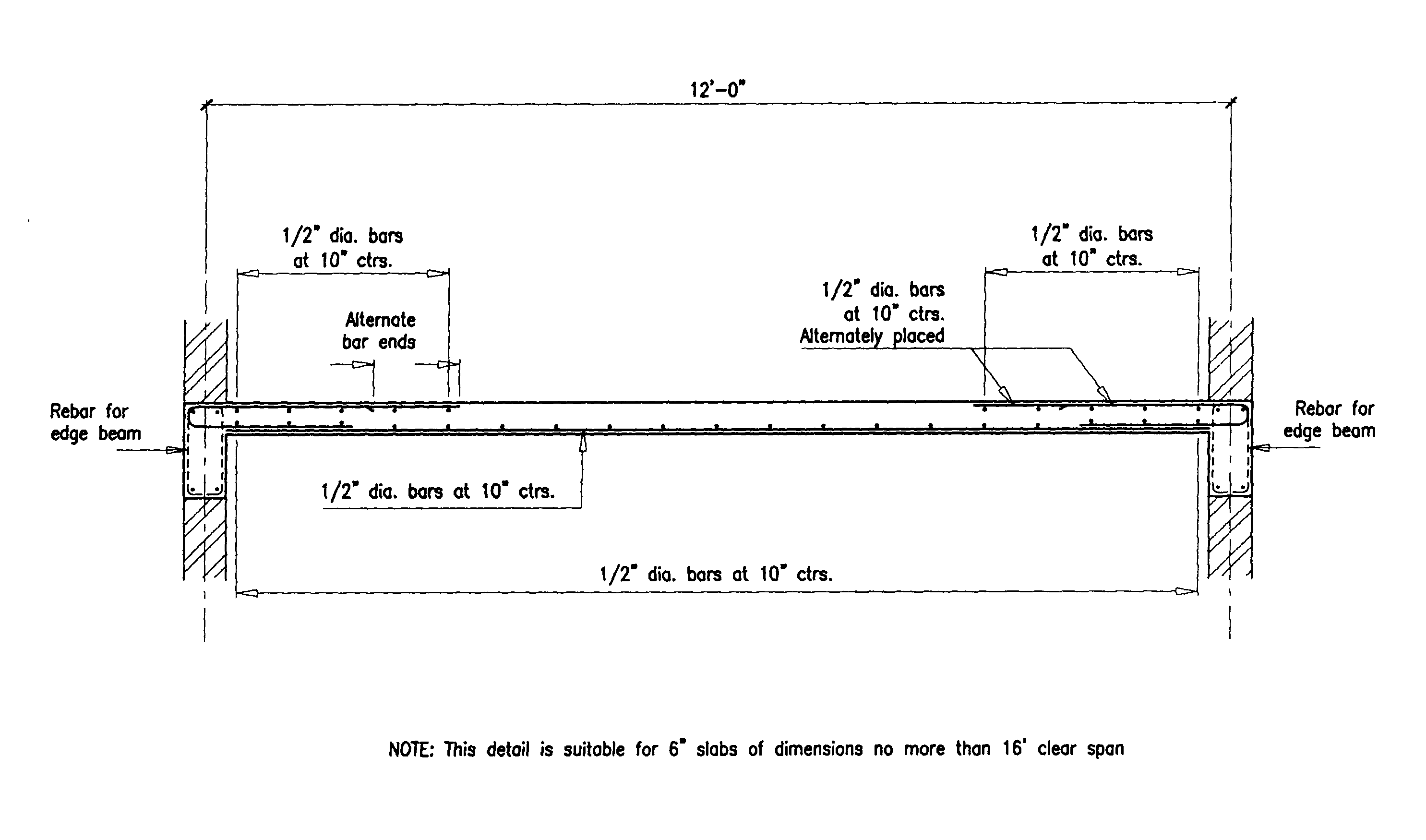



Building Guidelines Drawings Section B Concrete Construction
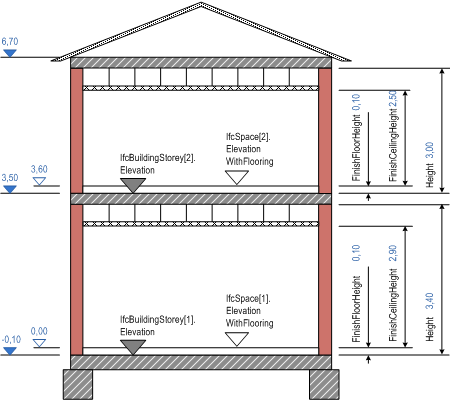



Ifcspace




Making Of Non Suspended Slab Kylieofthewang Youtube



Farm Structures Ch5 Elements Of Construction Floors Roofs



1




How Is A Ground Floor Slab Constructed
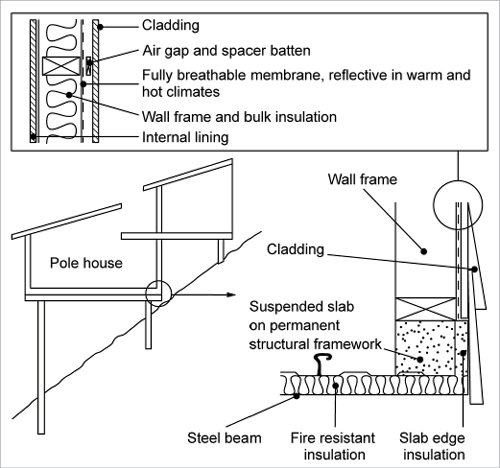



Concrete Slab Floors Yourhome




Response Of Building Systems With Suspended Floor Slabs Under Dynamic Excitations Sciencedirect




Slab




Building Standards Technical Handbook 17 Non Domestic Buildings Gov Scot



Insulation For Solid Concrete And Suspended




Q A Solid Wood Floors Over Concrete Slabs Jlc Online




Beam And Infill Suspended Floors Designing Buildings Wiki




A Combinatorial Optimization Approach For Multi Hazard Design Of Building Systems With Suspended Floor Slabs Under Wind And Seismic Hazards Sciencedirect
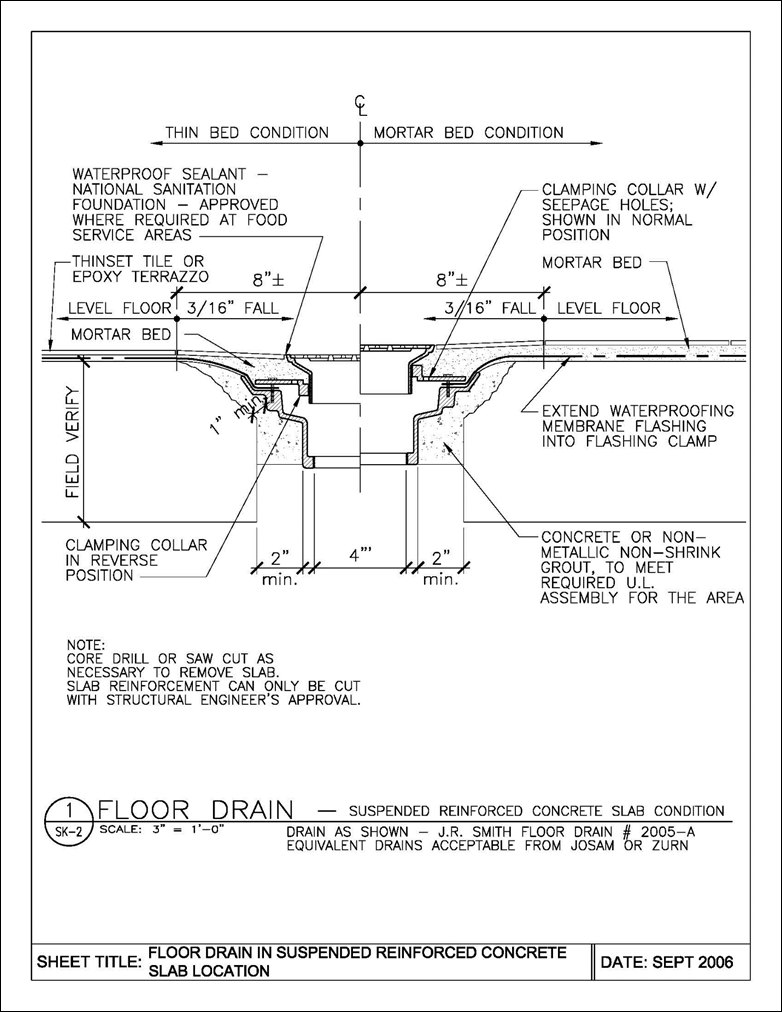



7 4 Floor And Wall Coverings




Response Of Building Systems With Suspended Floor Slabs Under Dynamic Excitations Sciencedirect




Ct 1 Assignment
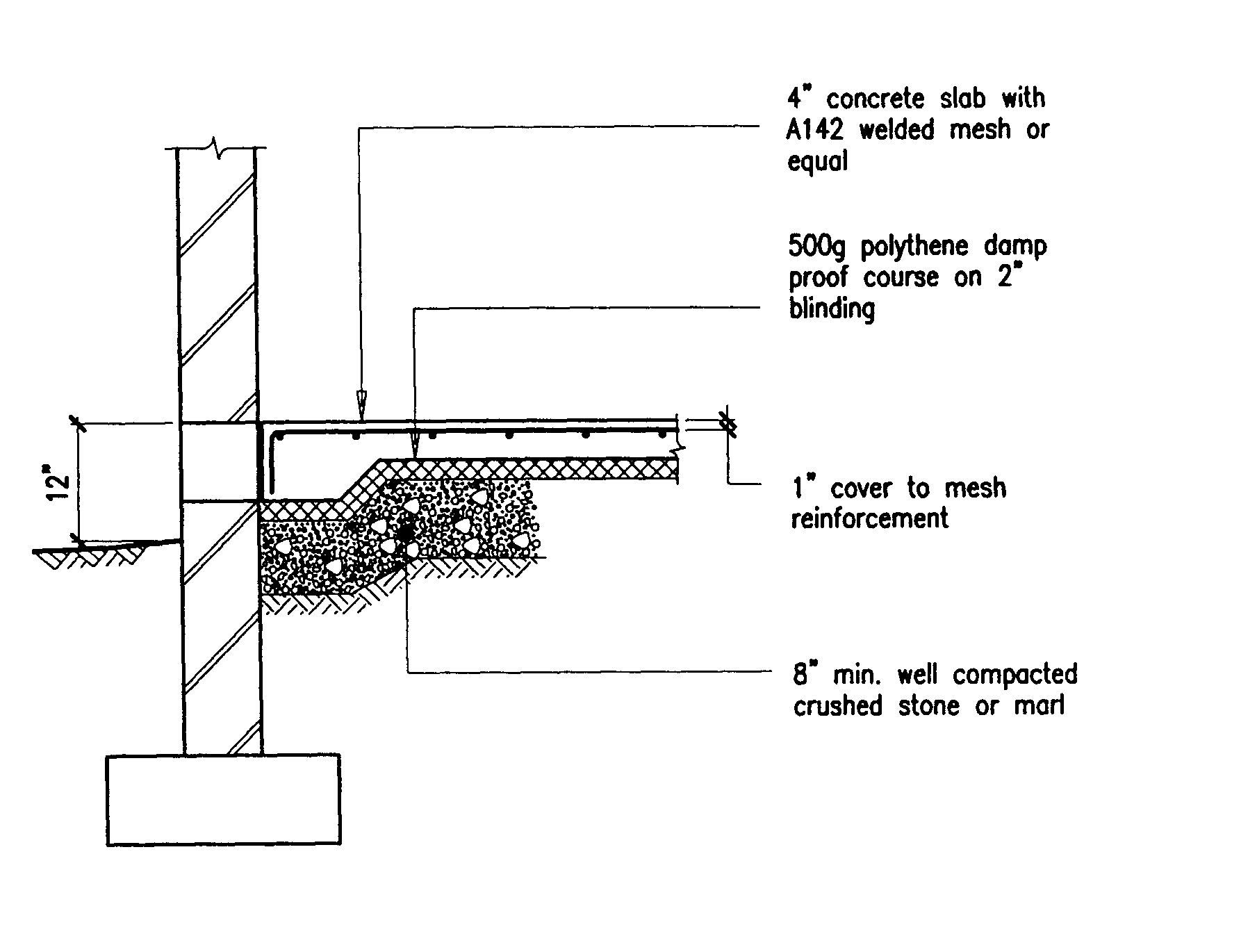



Building Guidelines Drawings Section B Concrete Construction




Non Suspended Slab Non Suspended Slab الهندسة والمعلومات Facebook




Pdf Slab And Floors Cracks And Crazing Identified There Types And Way To Repair




Build Diy Suspended Concrete Ground Floors



Building Guidelines Concrete Floors Slabs




Builder S Engineer Design Example Piled Ground Beams With Suspended Slab




Method Statement For Construction Method Statement Non Suspended Slab




One Day Seminar On Design Detailing Specification And Construction




Suspended Floors All You Need To Know Thermohouse




Builder S Engineer Suspended Ground Floor Slabs




Suspended Slab For Housing On Expansive Clay Download Scientific Diagram
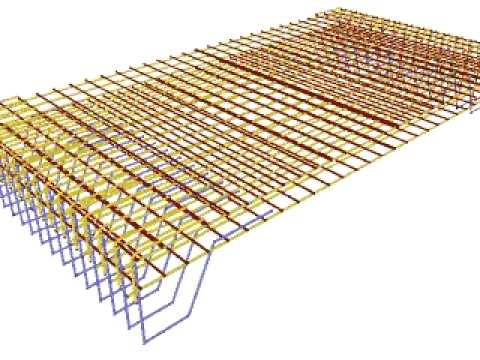



Suspended Ground Floor Slab Reinforcement Avi Youtube



Suspended Slab
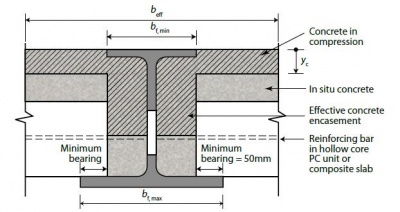



Floor Systems Steelconstruction Info




Concrete Slab Wikipedia
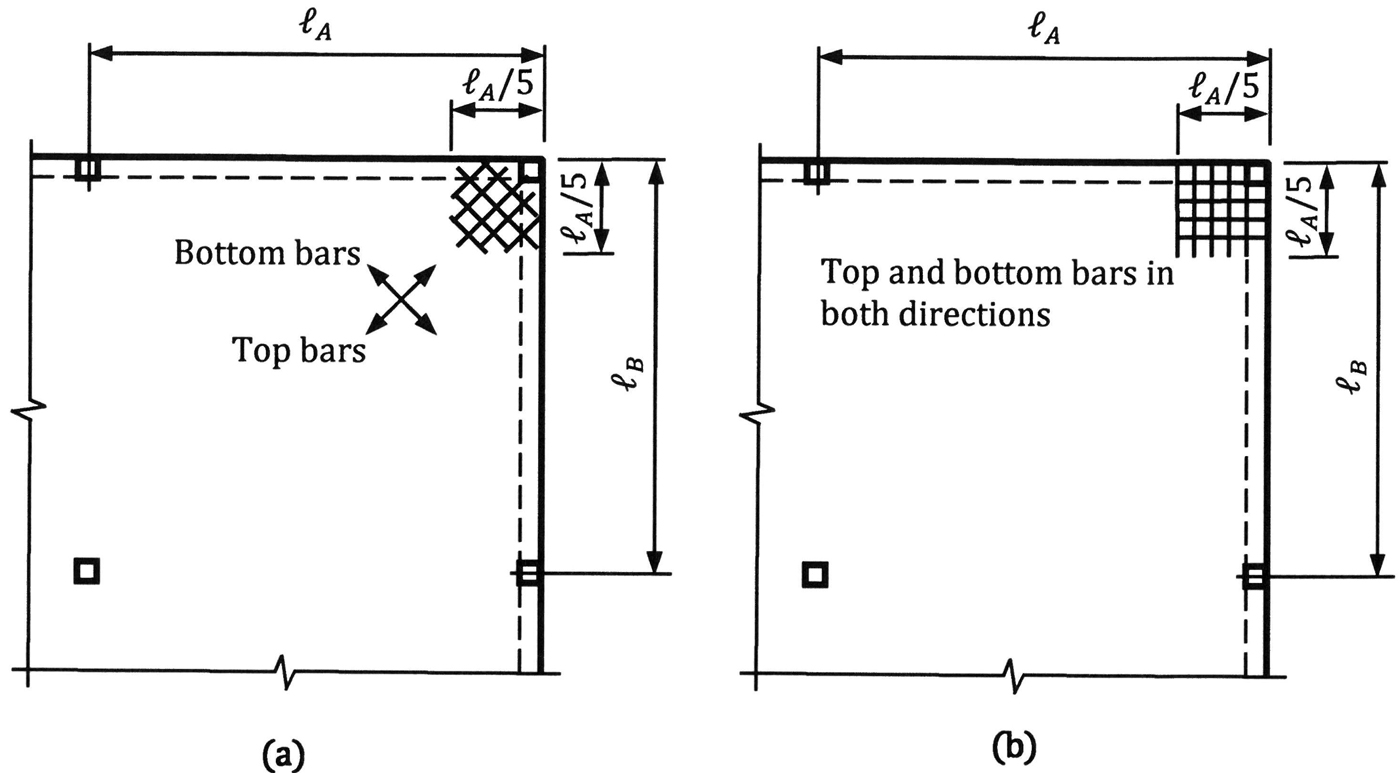



Structure Magazine Recommended Details For Reinforced Concrete Construction
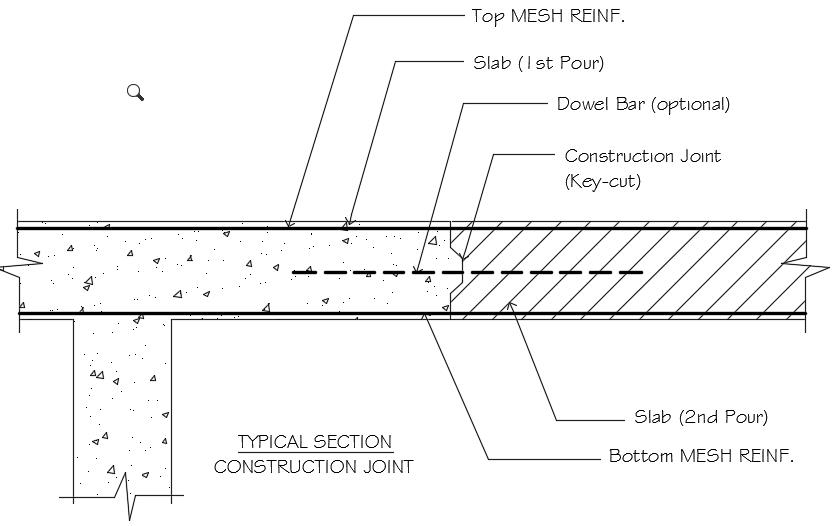



Construction Joint In Slabs The Structural World
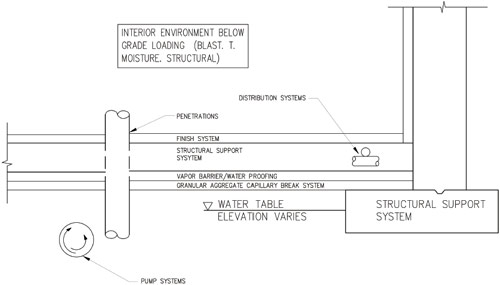



Floor Slabs Wbdg Whole Building Design Guide
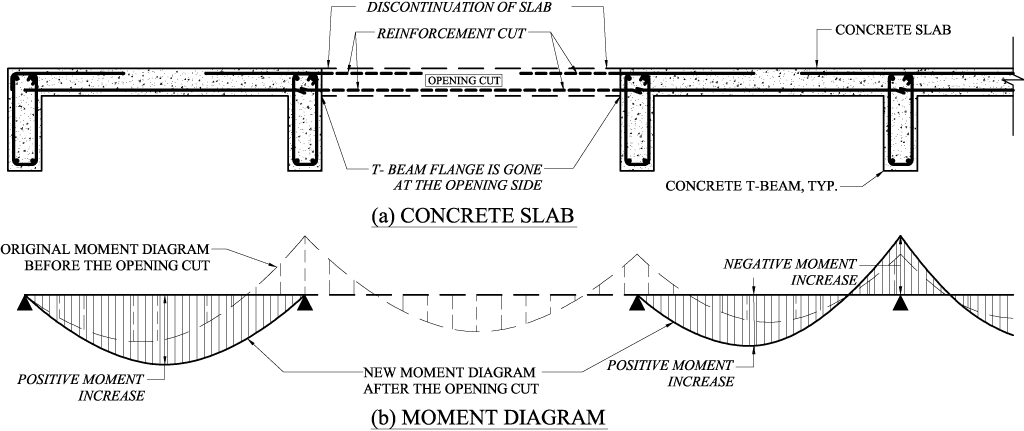



Structure Magazine Creating An Opening In Existing Floors




Eurima Suspended Concrete Floors
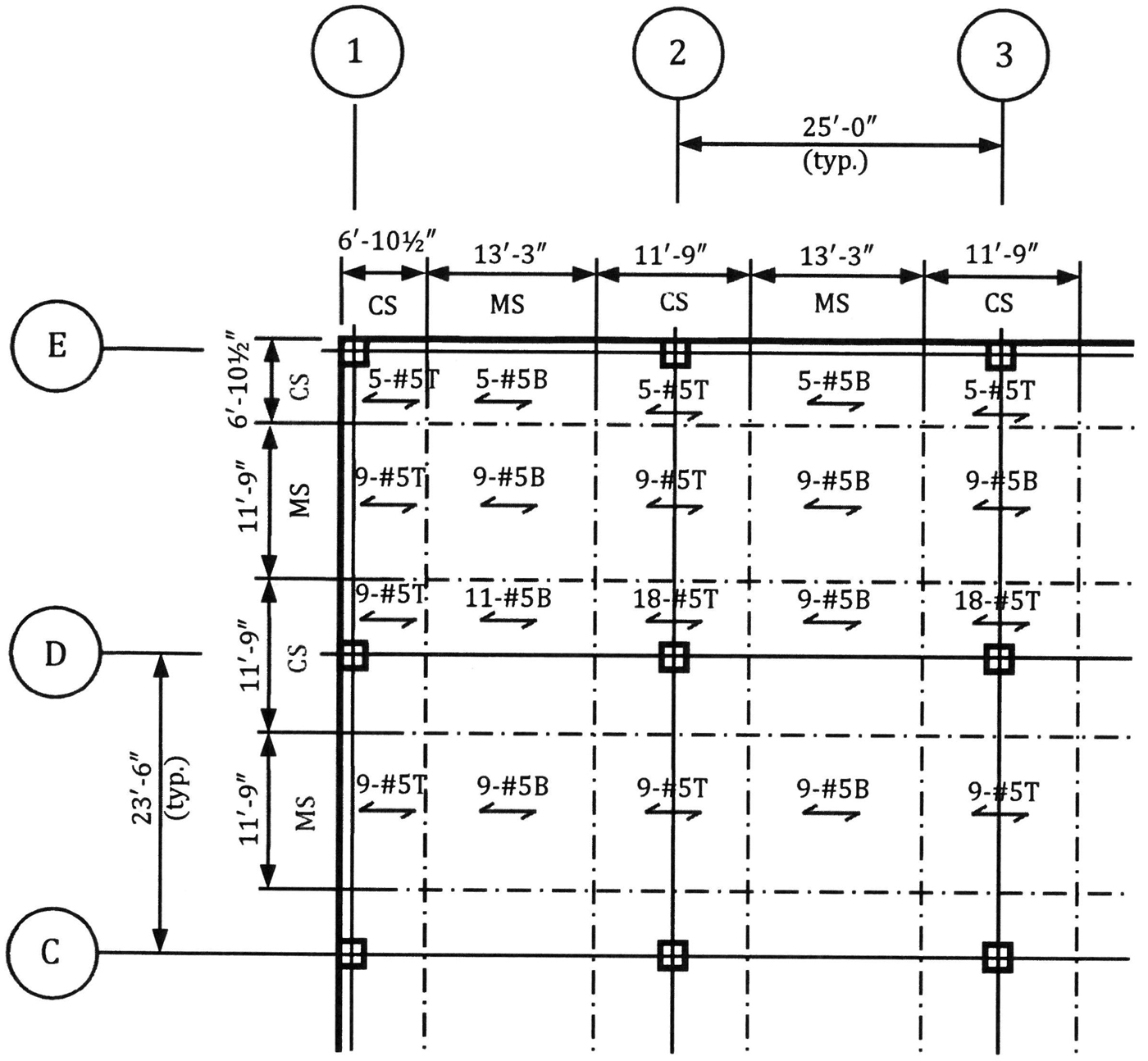



Structure Magazine Recommended Details For Reinforced Concrete Construction




Sarawak Edition Struktur Lantai Mengikut Kaedah Facebook




Slab On Ground Concrete Calculations Youtube




Non Suspended Slab Is A Slab That Cast On The Ground The Method To Design This Slab Is Different Than Suspended Slab How To Design A Non Suspended Slab Quora




Topic 2 Measurement Suspended Floor Slab Pdf Concrete Materials
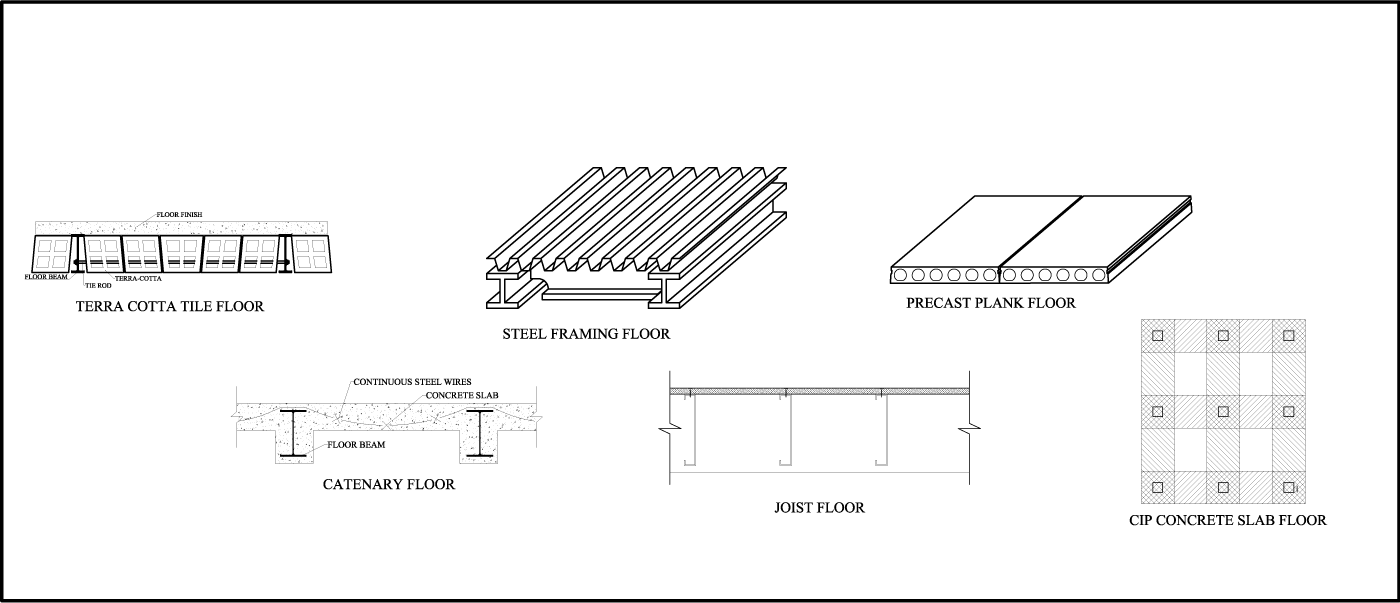



Structure Magazine Creating An Opening In Existing Floors



What Is The Importance Of A Reinforced Concrete Slab



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿